Solar panels are truly the best way to receive all that efficient renewable energy. The amount of available space determines how many solar panels you can install in your house.
However, as per the recent trends in 96-cell technologies, it is said that solar panels will have smaller dimensions while offering a higher output. Manufacturers like Panasonic have created solar panels of a smaller size and increased power output.
It is likely for this trend to be common in the coming time. To find out more about the same, read ahead. Today, we will tell you everything about the possibility of solar panels getting smaller and thus, becoming more efficient.
Contents
- 1 Key Takeaways
- 2 Can Solar Panels Become Smaller?
- 3 What Are The Factors Affecting The Size Of Solar Panels?
- 4 Can We Have Thinner Silicon Cells To Reduce The Size Of Solar Panels?
- 5
- 6 Case Study: Solar Panel Installation with Smaller, More Efficient Solar Panels
- 7 Expert Insights From Our Solar Panel Installers About Solar Panels Getting Smaller
- 8 Experience Solar Excellence with Us!
- 9 Conclusion
Key Takeaways
- Solar panels are becoming smaller while offering higher power output, driven by advancements in technology and manufacturing processes, with MIT and Panasonic contributing to this trend.
- The size of solar panels is influenced by factors such as the number of solar cells and their efficiency, and higher efficiency can lead to smaller panel sizes while maintaining power output.
- Researchers are exploring the possibility of reducing the size of silicon cells in solar panels to further decrease costs, making solar energy more affordable and environmentally friendly.
Can Solar Panels Become Smaller?
Most of us are used to having solar panels spread over a large area on our rooftops to receive heaps of renewable energy. However, research has suggested that solar panels can become smaller in dimension yet provide a lot of energy.
Recently, researchers at the MassachusettsInstitute of Technology (MIT) have come up with a solar panel that is extremely light and thin. These appealing features of the solar panel allow it to rest on a soap bubble without popping it.
The essential element of this solar panel lies in its manufacturing process that is responsible for producing the three important layers of the solar panel. The three layers are as follows –
- Baselayer
- Light absorbing layer
- Protective coating
The new solar panel by MIT researchers has eliminated all the space that is existent between these layers. This solar panel is a huge step in the development and advancement of renewable energy.
It has successfully reduced the production cost and also lowered the number of solar panels that you need to install at your house. Furthermore, it has also lessened the usage of expensive materials.
This newly-found feature of solar panels brought about by Panasonic and MIT will prove beneficial in the coming time as solar panels are used worldwide. Smaller solar panels will contribute to the reduction of capital and commercial costs.
Additionally, it will also reduce land costs as solar panels require a large availability of space. If you are a residential user of solar panels, this innovation will benefit you as well. It will certainly reduce the number of solar panels that you install on your rooftop.
Consequently, it will reduce the amount you pay for solar panels and their installation.
What Are The Factors Affecting The Size Of Solar Panels?
Solar panels are flexible when their size can be reduced substantially while retaining or increasing the energy they emit. However, there remain certain factors that affect or influence the size of solar panels.
Let’s take a look at these factors to determine whether it is a good idea to reduce the size of solar panels.
Quantity of solar cells
Every solar cell present in the solar panel enables the conversion of sunlight into electricity. The photovoltaic cells present in the solar panels can be manufactured in various sizes. The size of these cells can be small enough to fit within solar digital watches.
Nevertheless, it is important to note that a single photovoltaic cell cannot generate too much power. One photovoltaic cell can only produce up to 0.5V of power. Consequently, to produce more power, a series of solar cells are wired together.
This will ultimately lead to a higher voltage and, thus, higher power outputs. So, inferring from the information given above, solar panels are an assimilation of multiple photovoltaic solar cells. These cells are wired parallel in a series to increase the output of current and voltage.
The commonly available commercial solar panels typically come with 36, 60, 72, or 96 cells. As you may have already guessed, the number of cells in a solar panel will determine the size of a solar panel.
So, if there are more cells in a solar panel, the panel will have a greater length or width. In some cases, both the length and width might be large.

The efficiency of solar cells
The efficiency of a solar panel is the most important element that determines the output power and energy you will receive. Therefore, efficiency acutely affects the size of a solar panel and the power output that solar panels emit.
The concept of efficiency can be explained with the help of a simple expression. Take a look at it:
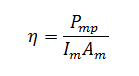
In the above-given formula, Pmp refers to the maximum powerpoint. Im refers to the incident isolation on the module, and Am refers to the module area.
To simplify this – when we increase the efficiency of a solar panel, the size or area will be reduced if we want to obtain the same power output, i.e., the Pmp.
It is no secret that the resultant efficiency depends on the type of technology used in the device. The commonly used monocrystalline solar panels can provide a total efficiency value between 20% and 22%. Solar panels by Panasonic and LG are known to feature this kind (20%) of efficiency.
Various solar cells have different efficiencies
Providers like Sunpower manufacture solar panels with a total efficiency of 22%. On the other hand, polycrystalline solar panels provide us with an efficiency of 17-18%. So, the final power outputs are also dependent on the kind of technology and the model of solar panels you use.
Other technologies like the single P-N junction silicon cells come with a maximum theoretical efficiency value – the Shockley-Queisser limit. The maximum efficiency of these cells is 33.7%. However, due to thermodynamic reasons, this efficiency cannot be surpassed.
This limitation means that the extent to which we can reduce a singular P-N junction solar panel is restricted. At this point, it is important to note that this efficiency value of 33.7% has been exceeded in laboratories in various tests.
Laboratory tests have revealed that multi-junction solar cells have reached efficiency values close to 50%. As appealing as this sounds, these technologies come with their issues.
For example, these technologies are not commercially available in the market because the manufacturers will have to bear the extra cost. The manufacturing costs are too high.
However, these technologies are used in the aerospace domain as maximum efficiency is the most important element in such fields. So, bearing the extra cost is not a barrier.
Can We Have Thinner Silicon Cells To Reduce The Size Of Solar Panels?
Solar panels are now available at very reasonable prices due to reducing the cost of renewable energy. Another reason for the popularity of solar panels is that they are extremely helpful for safeguarding the environment.
More and more research is being conducted to reduce solar panels’ cost further because solar panels can be highly effective in use worldwide.
Because of the same, researchers at MIT and National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) have delineated how costs can be slashed further by reducing the size of the silicon cells used in solar panels.
Of course, thinner silicon cells have been thought about before. However, this approach has faced multiple hurdles, such as the silicon becoming too fragile and brittle if slimmed. This might lead to significant losses at the time of manufacture.
Slimmed silicon cells will also resultantly give out lower efficiency and thus, a lower power output. Researchers today are looking into this by addressing these issues with the help of better equipment.
Developments in solar cell architecture are also contributing to the research that revolves around this concept. Researchers at MIT and NREL say that we need to be mindful of the economic considerations and technological advancements.
It is said that the affordability of solar panels should ensure a premium quality as well. Presently, the solar panel industry is growing at a rapid rate of 30% per year.
90% of the solar panels all over the world are made up of crystalline silicon. So, cutting down on the silicon used will reduce the cost of the entire solar panel structure that is used for efficient power output.
Case Study: Solar Panel Installation with Smaller, More Efficient Solar Panels
Background
The Barnard family in Indianapolis, Indiana, invested in solar energy to reduce their electricity bills and carbon footprint. With limited roof space and a growing interest in sustainable living, they were particularly interested in the latest advancements in smaller, more efficient solar panels.
Project Planning and Objectives
The Barnard family’s objectives were:
- Maximize energy production within a limited roof area
- Reduce monthly electricity bills
- Take advantage of state and federal incentives for solar energy
- Ensure a reliable and efficient solar power system for their home
They contacted Solar Panels Network USA for an assessment and installation plan tailored to their needs.
Installation and Costs
After a detailed evaluation, a 6kW solar panel system using high-efficiency, compact panels was recommended. The cost breakdown included:
- High-Efficiency Solar Panels: $14,000
- Installation: $3,000
- Inverter and Battery: $2,500
- Permits and Inspections: $1,000
- Total Estimated Cost: $20,500
Financial Incentives:
- Federal Tax Credit (ITC): $6,150
- State Rebates: $1,800
- Adjusted Total Cost: $12,550
Installation Process
The installation was completed over three days and included the following steps:
- Site Assessment: Evaluating the roof’s condition, orientation, and shading to determine the best placement for the panels.
- Panel Installation: Mounting 20 high-efficiency, compact solar panels on the south-facing roof to maximize sunlight exposure.
- System Integration: Connecting the panels to a high-efficiency inverter and a battery for energy storage.
- Inspection and Activation: Conducting a final inspection and system activation to ensure optimal performance.
Results and Benefits
The Barnard family’s solar power system now generates approximately 700 kWh per month, covering most of their energy needs and significantly reducing their reliance on the grid. Smaller, high-efficiency panels maximized the available roof space and optimized energy production.
Environmental and Financial Impact:
- Annual Savings: $1,800
- Payback Period: ~7 years
- Reduced CO2 Emissions: ~3.5 metric tons annually
- Enhanced Energy Independence: The family experiences fewer disruptions and significantly reduces energy costs.
Summary
The Barnard family’s experience in Indianapolis, Indiana, illustrates the substantial benefits of using smaller, high-efficiency solar panels. By leveraging advancements in solar technology and taking advantage of available incentives, they achieved significant financial savings and reduced their carbon footprint. Solar Panels Network USA’s expertise ensured a smooth installation process, demonstrating the effectiveness of customized solar solutions. This project highlights the growing trend toward compact solar panels, making solar energy more accessible and practical for homeowners with limited roof space.
Expert Insights From Our Solar Panel Installers About Solar Panels Getting Smaller
The trend toward smaller, more efficient solar panels is driven by advancements in technology. Manufacturers like Panasonic are already producing compact panels with higher output, making solar installations more space-efficient.
Reducing the size of solar panels without compromising their power output is a significant step forward. This allows for more flexibility in installation, especially in residential areas with limited roof space.
Future developments in solar cell efficiency, particularly with multi-junction cells, could lead to even smaller panels that offer the same or greater energy output, making solar power more accessible and cost-effective.
Experience Solar Excellence with Us!
Trust in Solar Panels Network USA, where our seasoned experts deliver top-quality solar solutions for homes and businesses nationwide. With a legacy of countless successful installations and a commitment to sustainable energy, we’re your reliable partner in the solar journey. Ready for a brighter, eco-friendly future? Call us now at (855) 427-0058 and harness the power of the sun!
Conclusion
With advancements in technology, it is highly possible to reduce the size of solar panels. However, as mentioned above, this is entirely dependent on the efficiency and the number of solar cells used in the solar panel.
Moreover, solar panels are on the rise due to the low cost of renewable energy. Hence, people will likely switch from buying a larger number of panels to buying small panels that provide high efficiency.
Solar panels that provide up to 22% efficiency are quite commonly used. With a little more research and development, the world will take a leap towards small panels with increased power output.
Of course, solar panels are a blessing in disguise for the environment and are also financially convenient. So, it is natural for researchers to come up with more developmental models that enhance the entire experience.
So, what are you waiting for? Get started with your goal to protect the environment and use solar panels for the best and most efficient renewable energy there is!